Published 23 April 2020
Young workers make up a disproportionate part of the service industries in the US, which have been hit hardest by the COVID-19 pandemic. As economies recover, the long-term plight of youth employment will need attention.
They are the ones who will bear the brunt of the coronavirus recession.
A little more than a decade ago, millennial college students graduated into what was then the worst economy in decades. In the United States, the Great Recession wreaked long-term damage on young people, many of whom faced slim job prospects along with mountains of student debt. Compared to earlier generations, these young adults today have less wealth, more debt and are less likely to be financially secure.
Today’s youngest workers could have it even worse. Young workers – who make up a disproportionate share of workers in hospitality, food service, retail and other service industries hit hardest by the COVID-19 pandemic – are likely to shoulder the worst of the coming recession.
Young workers: first to feel the pain
Young workers have been among the first to feel the pain as the restaurant, retail, and hotel industries reel from the initial impacts of the pandemic. Marriott, for instance, has furloughed tens of thousands of employees. So, too, have Hilton and Hyatt. Many small businesses are forced to close shop or lay off most of their workforce. The National Restaurant Association reports that business dropped by nearly half among its members just in the first half of March.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, workers between the ages of 20 and 24 account for nearly one-third of restaurant waitstaff, one-fourth of all retail cashiers, and one-fifth of all retail salesclerks. Young workers also occupy a large share of other entry-level service jobs in entertainment and hospitality, such as hotel and motel desk clerks (one-third), ushers and ticket-takers (one-fifth) and baggage handlers (one-sixth).
Young people also make up a disproportionate share of the low-wage workforce hardest hit by the pandemic, period, according to new research from the Brookings Institution. Scholars Martha Ross, Nicole Bateman, and Alec Friedhoff find that workers ages 18 to 24 comprise nearly one in four low-wage workers, with the most common occupations being retail, food service, and lower-level administrative support. Many of these young workers can ill afford any loss of income: Among the 13 percent who lack a college degree, the median hourly wage is just US$8.55. Worse yet, one in five of these workers is the sole earner in their family; 14 percent are also caring for children.
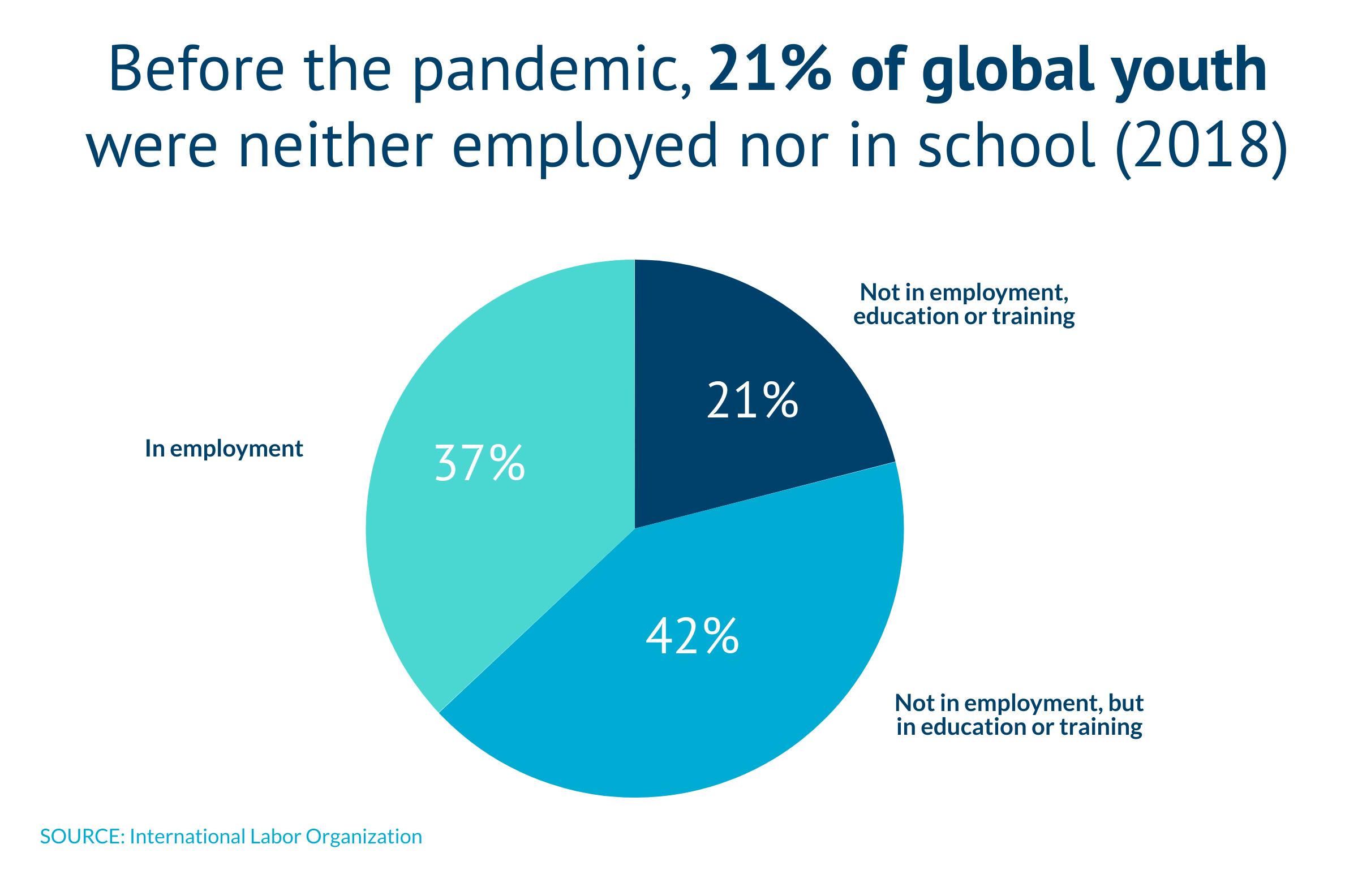
A new crop of “not in school, not working”
Even before the current crisis, many young people were already in dire economic circumstances. According to the Social Science Research Council, as many as 4.5 million young adults ages 16 to 24 were not in school nor working in 2017, the latest year for which data are available. No doubt this figure has already skyrocketed.
Unfortunately, unemployment might be only the start of young workers’ worries in the coming months.
The sudden closure of colleges and universities means that multiple cohorts of students are missing out on opportunities to lay the foundations of their future careers. “Job fairs and internships have been called off, as have debating competitions, graduate school admission tests and conferences that are essential opportunities to network and get jobs,” writes The Hechinger Report.
A different economy after COVID
Other hazards also loom in the future job market that could disadvantage younger workers. For instance, the pandemic may also accelerate the push to automation, as researchers Mark Muro, Robert Maxim and Jacob Whiton of the Brookings Institution argue, which would also hit younger workers the hardest. According to their analysis, as many of 49 percent of workers ages 16 to 24 are in jobs vulnerable to automation.
Moreover, the current massive disruptions in higher education and in business likely also mean that skills gaps will worsen as training programs are put on hold and businesses struggle simply to survive. Shortages of qualified workers will not only significantly hamper recovery efforts in the future but handicap current industries’ efforts to retool themselves to a radically changed environment.

Worldwide impacts for youth workers
The same story is playing out globally. According to the International Labor Organization (ILO), young people are roughly twice as likely to be unemployed compared to adults. After the global recession in 2009, adult employment grew uninterrupted but the number of young people employed contracted by more than 15 percent. In 2018, 21.2 percent of global youth were neither employed nor in education and training.
The COVID-19 pandemic is inducing a global labor shock both because workers cannot carry out their jobs and may have lost their jobs, but also because consumer demand especially in services industries has fallen off and could be slow to return to previous levels. In a vicious cycle, billions in lost labor income will further suppress consumption of goods and services. At the beginning of April, the ILO estimated global unemployment would rise between 5.3 million and 24.7 million, but with 22 million Americans alone filing for unemployment over the last four weeks, this estimate is already vastly inaccurate. The long-term damage to young workers’ prospects is incalculable.
What next?
Economies around the world are already responding with rescue packages aimed at blunting some of the economic hardship the pandemic is creating. But as the crisis wears on and, with luck, economies can begin to recover, the long-term plight of young workers will need much more attention.
© The Hinrich Foundation. See our website Terms and conditions for our copyright and reprint policy. All statements of fact and the views, conclusions and recommendations expressed in this publication are the sole responsibility of the author(s).



